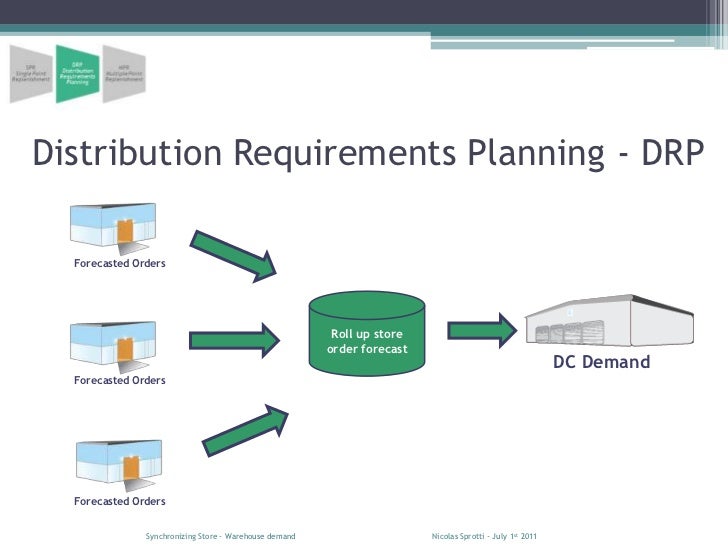
Distribution requirements planning (DRP) is a systematic process to make the delivery of goods more efficient by determining which goods, in what quantities, and at what location are required to meet anticipated demand. The goal is to minimize shortages and reduce the costs of ordering, transporting, and holding goods.
Also known as distribution replenishment planning, DRP is a time-based approach that determines when inventory is likely to be depleted and plans replenishment to avoid shortages. DRP uses a tree-like structure where a central facility, such as a warehouse, supplies regional facilities which then supply other facilities in the tree. This structure can contain any number of layers.
A key element of DRP is the DRP table, which usually includes elements that are important in the process, including:
- forecast demands
- current inventory levels
- target safety stock
- recommended replenishment quantities
- replenishment lead times
DRP distribution works by either a pull or push method. The pull method has goods move up through the network by fulfilling customer orders. This provides more availability for consumers because local management controls the availability of the goods. However, managing distribution inventory can be difficult because every order is new to the supplying location as demand flows up the network. This is called the "Bullwhip Effect:" small changes in consumer demand that generate large swings in demand higher up the network.
In contrast, the push method sends goods down through the network. It generally has lower costs because shipments are planned globally and stored centrally. However, service levels can suffer if central planning is too far removed from the actual demand.
DRP ideally combines the service levels of pull with the efficiency of push, but this depends on accurate forecasts and stable processes to be successful. If both of these exist, DRP produces high fulfillment performance with minimal inventory. Companies usually try to hedge their bets by using safety stock, but that can reduce the overall effectiveness of the DRP strategy, resulting in higher inventory levels or shortages.
A number of vendors include DRP modules in their ERP software.